Armies and Autocrats: Why Putin’s Military Failed
by Zoltan Barany
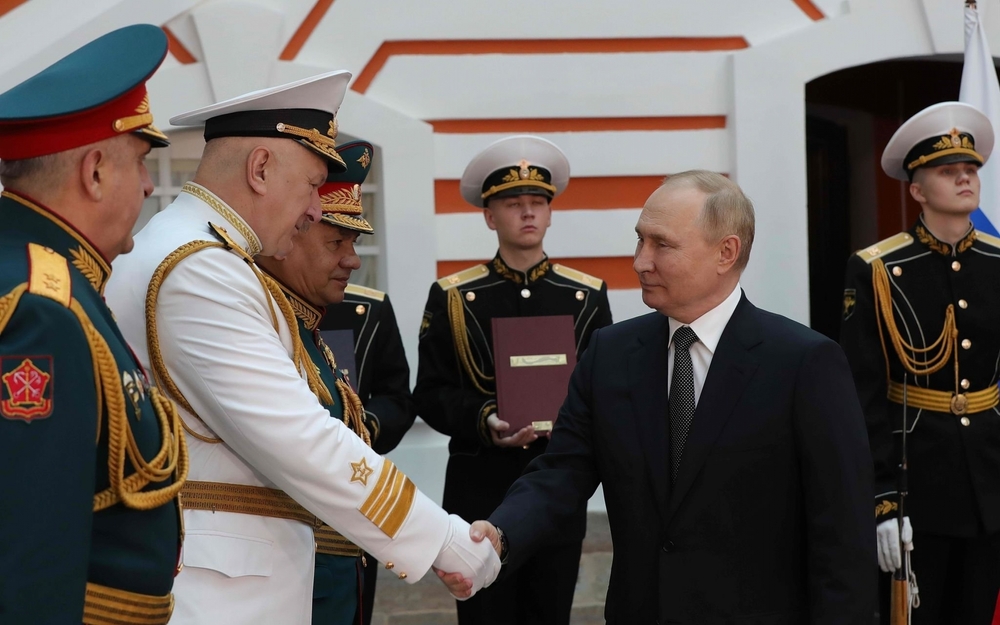
AbstractThis essay analyzes the failure of Vladimir Putin’s military in Ukraine in terms of five key factors. The first of these is Putin’s monopolization of control over the armed forces, which has driven critical voices and honest debates out of military and defense matters. Second is the failure of reform: Efforts to overhaul the bloated, ill-equipped post-Soviet military have not produced a twenty-first century fighting force that can match the world’s best armies or counter their capabilities. Third, Russia’s military has been unable to attract talented young people. Fourth, Russia’s mammoth defense industry produces too few weapons, and those it does turn out cannot match sophisticated Western arms. Finally, the operations in Georgia, Crimea, and Syria were conducted against feeble adversaries and said zero about how Russian forces would perform in a conventional land war against a resolute, well-armed enemy. In short, the Russian military is a reflection of the state that created it: Autocratic, security-obsessed, and teeming with hypercentralized decisionmaking, dysfunctional relations between civilian and military authorities, inefficiency, corruption, and brutality. Before and even shortly after Russian president Vladimir Putin invaded Ukraine on 24 February 2022, most experts predicted that Russia’s military would make short work of its southwestern neighbor’s defenders. The conventional wisdom held that while Russia’s forces had fallen on hard times after the Cold War, Putin’s more than two decades of rule had transformed them into an effective military machine. In early 2014, Russian troops in unmarked green-camouflage uniforms had taken Crimea from Ukraine with little bloodshed or even exertion. Two years later, one analyst called the intervention of the Russian Air Force on the side of the Bashar al-Assad regime in Syria “the most spectacular military-political event of our time.” In 2021, another commentator pointed to successful campaigns not only in Ukraine and Syria but also in Georgia (2008) while crediting Putin with having “overseen a thorough transformation of the Russian Armed Forces.” Flawed appraisals such as these are based on a misunderstanding of Russia’s military landscape. The Russian military is a quintessential reflection of the state that created it: Autocratic, security-obsessed, and teeming with hypercentralized decisionmaking, dysfunctional relations between civilian and military authorities, inefficiency, corruption, and brutality. We should note five key points. The first is that Putin’s monopolization of control over the armed forces and refusal to allow an independent legislature have driven critical voices and searching, honest debates out of military and defense matters. Second is the failure of reform—as the world can now see, efforts to overhaul the bloated, ill-equipped post-Soviet military have not produced a twenty-first–century fighting force that can match the world’s best armies or counter their capabilities. Third, Russia’s military has been unable to attract talented young people. Senior officers stubbornly refuse to delegate authority, robbing juniors of chances to develop initiative and leadership qualities, while most noncommissioned officers (NCOs) and their troops are poorly prepared. Fourth, Russia’s mammoth defense industry—largely owned and run by the state—produces too few weapons, and those it does turn out cannot match sophisticated Western arms. Finally, the operations in Georgia, Crimea, and Syria proved nothing: They were conducted against feeble adversaries and said zero about how Russian forces would perform in a conventional land war against a resolute, well-armed enemy. In a constitutional democracy, the legislature and the executive are both involved in controlling the armed forces. The chain of command is codified, as are respective institutional responsibilities vis-`a-vis the military. Laws likewise prescribe the potential uses of the military in various domestic and external scenarios. The national legislature passes the defense budget and supervises its disbursement, the chief executive acts as commander-in-chief, the defense minister is not a serving officer, and civilians—including those in the media and defense-focused NGOs—offer advice and scrutiny. In authoritarian states, the executive directly controls the military while the national legislature (if one exists) and regional authorities have no say. There is no safe place for independent security-policy experts, scholars, or journalists to function. The Kremlin runs the Russian armed forces, and today the Kremlin means Putin. He has few confidants. Since 2012, his principal advisors in the security realm have been Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu (who has no military background) and General Valery Gerasimov, the armed forces chief of staff. They serve entirely at the pleasure of the president—who summarily dismissed each man’s predecessor. Putin’s frustration with the Defense Ministry’s handling of the “special military operation” in Ukraine (to say “war” or “invasion” can bring a Russian citizen years in jail) has led to the marginalization of Shoigu, who nonetheless has kept his job despite strident criticism from prominent Russian nationalists. When Putin came to power in 2000, the military and its top brass held considerable sway over foreign and defense policy, military reform included. Since then, Putin has wrestled control of all military and security forces into his own hands. During Defense Minister Anatoly Serdyukov’s tenure (2007–12), bloodless purges removed from the general staff officers who disagreed with the Kremlin’s ideas about military reform, who were thought too independent-minded and unwilling to give Putin constant support. Serdyukov cut the Central Military Administration staff by more than 30 percent, mostly getting rid of generals and colonels. For the last dozen years, Russian generals have been Putin’s servants. Their careers depend not merely on their professional competence but on their personal loyalty to him. On paper the Defense Ministry answers to parliament and its committees on defense and security, but in practice the ministry answers to the Presidential Administration alone. The president decides whether, when, where, and how to deploy the military, at home or abroad. Putin is a centralizer; while Russia remains nominally federal, local councils have lost capacity to perform even traditional tasks such as calling up reservists, as recent events have shown. Journalists who have dared to write objectively on defense issues have been hit with heavy jail time even for open-source reporting. Membership in NATO—a defensive alliance espousing liberal-democratic principles—may constrain an authoritarian such as Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orbán from seeking to “adjust” his country’s borders, but Putin faces no such obstacle. He dominates the Collective Security Treaty Organization (comprising ex-Soviet republics), while the “dictators’ club” that is the Shanghai Cooperation Organization in no way constrains his grip on the Russian military. For more than a decade, Russia’s army has been indisputably Putin’s army; no trace of institutionally balanced civilian authority, transparency, or accountability impedes his control over it.Reform InterruptusAt the Cold War’s end, Russian political and military leaders were aware of their forces’ shortcomings. For most of the 1990s, however, little happened beyond a reduction in force size. Generals opposed structural changes, political elites lacked the will to push back, and resources were scarce. The Russian army won the First and Second Chechen Wars (1994–96; 1999–2009) against a tiny breakaway region, but with an operational performance that was embarrassing. The August 2008 defeat of Georgia, another small and underfunded neighbor, also underlined Russia’s military deficiencies. Systems for command, control, communications, and intelligence performed so poorly that at times officers had to borrow war correspondents’ cellphones to reach troops. The air force admitted that it had four aircraft downed during the twelve-day conflict (the Georgians claimed to have shot down 21), losses that would have easily been avoided had unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs or drones) been on hand to fly reconnaissance. Russian sources acknowledged that tanks and warplanes had seen no overhaul since the Afghan War (1979–89), “smart” weapons and modern communications systems had been unavailable, and the Defense Ministry had relied on “favorite suppliers” known for making obsolete armaments. In response to such weaknesses, the reform program begun in 2008 sought to turn a Soviet-legacy military still based on mass mobilization into a leaner, more professional force ready for combat. Even if Ukraine has laid bare their limits, the changes made since 2008 have been considerable. With carte blanche from Putin, Defense Minister Serdyukov pensioned off or cashiered enough stubborn senior officers to break institutional resistance. The military’s structure was rationalized and streamlined. The number of large units shrank from 1,890 to 172, while 65 military colleges became ten and sixteen Soviet-era military districts became four. A main purpose of the defense reforms was to bridge the deep qualitative gap between Russian and NATO military personnel that the brief Russo-Georgian War had highlighted, or at least to improve the training and combat readiness of the nonelite troops who have always filled most Russian units. Modernizers also wanted to stabilize the army’s troop strength at a million. Russian official data are best treated with skepticism, but it appears that the total personnel strength of the Russian armed forces (land, naval, and air) has been between 700,000 and 900,000 over the past decade. Serdyukov reduced the size of the officer corps, phased out praporshchiki (roughly equivalent to warrant officers), and drastically increased the number of “contract” (professional) soldiers. In a bid to make professional soldiering more attractive, money went to improve the working conditions, housing, welfare, and pensions of servicemen and their families. Shoigu carried on the reform process, raising the number of contract soldiers to 410,00 by 2020, when conscripts in uniform numbered only 260,000. The conscripts are a token of Russia’s limitations: The Kremlin would like to have a fully professional military but cannot afford it, so the draft is needed to fill the ranks. The reform plan called for a half-million contract soldiers by 2019, but only 405,000 were said to have been signed up and that figure is likely inflated. As of 2012, contract soldiers were paid 25 percent more than the average Russian civilian, and military benefits were comparatively generous as well. But inflation has been a key problem. Its erosion of contract soldiers’ pay and benefits has made military careers less enticing and driven down applicant quality: The military has been chasing not only fewer but less desirable recruits. Without able contract recruits, the dream of a high-quality, NCO-enabled Russian military can never come true. A traditional weakness of Soviet or Russian armies going back to czarist days has been the absence of career NCOs. A modern military relies on professional “noncoms”: They enjoy significant autonomy; keep commissioned officers and enlisted personnel working together; and give to the troops training, discipline, and (not least) hands-on leadership “at the sharp end.” Russia’s military reform recognized the need for a professional NCO force; within ten years after the Georgian campaign, contractors predominated in what were considered NCO billets. But questions remained about the depth of their training and the degree of initiative accorded them in an army where the idea of delegating authority downward has long been a foreign concept. In 2009, the Defense Ministry established an NCO academy, but the two-thousand graduates that it produces each year do not seem to have been enough to transform army culture. In 2010, seventy-thousand of the junior officers whom Serdyukov had discharged had to be recommissioned in order to keep doing what in the West would be classed as NCOs’ jobs. The available data suggest, and the war in Ukraine has confirmed, that Russia is a long way from fielding the kind of proficient NCO force that is essential to a modern military, and which Ukraine itself is increasingly displaying through its own performance under arms. Reform never even touched other areas. These include combat medicine, something that Western armies have worked hard on in recent decades. Quickly bringing together wounded soldiers and critical care is key, but the Russian military with its history of tolerating high casualties has focused little on this. Young Russian army doctors who resigned their commissions protested that they had been issued “practically nothing” to work with in terms of equipment and could “provide only first aid.”Generals and SoldiersLack of trust in subordinates and reluctance to delegate mark every command level of the Russian military. The Soviet-era practice of waiting for orders to filter down from headquarters—a custom meant to leave no room for independent thinking and creativity—often results in missed opportunities on the battlefield. Serdyukov dismissed or eased out about a third of senior officers, including the last group of critical thinkers who might have disagreed with Kremlin policy. He made senior generals’ promotion prospects depend on their ability to read the signs emanating from the Presidential Administration. Even at the top of the military hierarchy, generals are wary of taking initiative for fear of angering superiors who now include Putin himself. Nonetheless, it seems that some in the high command did question Putin’s plan going in, especially the idea of a lightning strike to seize Kyiv, warning that Russian troops and equipment were not up to the task. When the doubters turned out to be correct, the Kremlin apparently allowed these generals to draw up a new strategy. They then turned the conflict into a war of attrition based on the old Russian standby of overwhelming firepower. When massed artillery and aerial bombardment failed too, as fighting around the vital southern city of Kherson and Ukrainian breakthroughs in other sectors showed, Putin shook up his roster of senior commanders three times. In April, in June, and again in September, the Kremlin changed generals in search of better combat performance. In early October, Putin gave General Sergei Surovikin the task of turning the war around even as Ukrainian forces carried on with counterstrikes around the flanks and into the rear areas of surprised Russian formations. Surovikin’s qualifications include experience in complex combat environments as well as a reputation for “total ruthlessness,” “corruption and brutality,” and mistreating subordinates. In other words, he promises to be a perfect fit for Putin and his army. We can also see Putin’s distrust of his high command in his ever deeper personal involvement in military decisions. As the Ukrainians counterattacked in September 2022, he told his generals that he himself would now set strategy. His micromanagement of the war extends to making low-level tactical decisions and giving orders to frontline generals from the Kremlin. According to Western intelligence sources, the Russian president “is making operational decisions at the level of a colonel or brigadier,” helping to determine the movements of forces and ordering stands “at all costs” (an approach that leads to troop and equipment losses as units banned from making tactical retreats fall prey to encirclement). Putin’s heightened involvement likely stems from his realization that early in the war his commanders kept him in the dark about how badly Russian forces were faring against unexpectedly nimble and fierce Ukrainian resistance. But should Putin, who has no military background, ever have expected his forces to do well in Ukraine? Starting in 2008, military education and training of all ranks did improve. There were more drills, including large-scale joint exercises featuring tens of thousands of personnel from different Russian services. Beefed-up flight hours for military aviators and improved maintenance routines for their aircraft reduced mechanical failures and combat losses in Georgia and Syria. To put all this in context, however, it must be stressed that outside a few elite units, Russian training and maintenance standards across the board have never been more than modest, and hardly reach the levels that characterize the world’s top militaries. Despite pay raises, the Russian armed forces have been unable to attract the best and brightest of young Russians in the face of competition from the civilian labor market. Housing remains a problem for officers with families, and for years pay has not kept up with inflation. In many units, conditions are poor and junior officers are treated with contempt as superiors play favorites. Anecdotal evidence suggests that many officers with employment opportunities outside the military resign their commissions. The 2018 decision to revive the post of zampolit (political officer) in units as small as infantry companies harks back to the Soviet era and signals that the state doubts its soldiers’ loyalty. Mandatory military service has been unpopular. Many of those who can afford to avoid it (by bribing army doctors to declare them unfit) do so, while the most desperate flee the country or even deliberately injure themselves to evade the draft. The brutal hazing of raw recruits, sometimes with tragic results, remains a problem despite efforts to curtail it. In 2008, the period of mandatory active service was halved to a single year, which means that after training a soldier is available for just six months of duty. Most troops that the army considers combat-ready are not draftees, though (perhaps surprisingly) conscripts make up about a quarter of elite commando units. The army planned to reduce its intake of conscripts to 150,000 by 2021, but missed that goal. As the Ukraine war grinds on, unwilling draftees will become more common, and the army will increasingly have to rely on poorly trained and motivated soldiers. Putin’s 21 September 2022 call-up of 300,000 reservists put new focus on manpower issues just ten days before the beginning of the fall conscription period. Many experts believe that mobilizing hundreds of thousands of reservists will prove exceedingly difficult. So far, the call-up has fallen disproportionately on ethnic minorities. These include nomadic reindeer herders from northeastern Yakutia (5,600 kilometers from Kyiv) as well as the Crimean Tatars, long repressed by Soviet and Russian regimes and vocal opponents of the peninsula’s annexation. Even if those mobilized are actual reservists, it is likely that only a fraction of them have had regular training in the years since they left active duty. It will be months before these troops can add to Moscow’s war effort. In a September 29 video call with advisors, Putin publicly admitted “mistakes” such as call-ups of fathers with children, people with chronic illnesses, and some over military age. Mobilized soldiers, some of them middle-aged, have complained that they were kept in “cattle conditions,” had to buy their own food, and received ill-fitting boots and uniforms as well as old, poorly kept weapons. The president left it to regional governors and officials below them to fix the problems, not mentioning that his own policies have undermined local governments’ capacities. During the first week after the mobilization declaration, at least 200,000 young Russians and their families absconded to neighboring countries including Kyrgyzstan and Mongolia, as well as farther afield. The absconders were joining millions of their fellow citizens, many of them young and highly educated, who have voted with their feet against Putin’s war. In recent years, elite troops and private military firms in Moscow’s employ have done much of Russia’s fighting. The best known among the latter is the Wagner Group, a mercenary outfit possibly named for the German composer and established in 2014 by Dmitri Utkin, a former special-forces lieutenant-colonel, and Yevgeny Prigozhin, an oligarch from Putin’s inner circle with multiple Soviet-era criminal convictions. The unit is allegedly overseen by Russia’s military-intelligence agency, the GRU, in which Utkin served. How Wagner gets paid remains murky, but funds likely come from state sources as well as oligarchs. Wagner operatives in their insignia-free uniforms were the “little green men” who first appeared during Putin’s Crimea takeover, and since then have taken part in armed conflicts in Syria as well as several African states including Libya, Mali, Mozambique, and Sudan. Reportedly, more than a thousand Wagner mercenaries have deployed to Luhansk Oblast in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine and have suffered heavy casualties. Wherever they go, human-rights violations and war crimes follow.Failings of a State-Run Defense IndustryThe Russian state is the main owner of the industries that yield most of its income (energy, banking, arms, and transport) and is directly involved in running them. As state-owned corporations, defense companies enjoy cheap credit, debt relief, and freedom from competitive market pressures. Although the state has invested heavily in the defense industry and has seen success in some areas, on balance Russia’s arms makers have failed to narrow the distance—and especially the quality gap—between their wares and those of the world’s leading weapons producers. Starting around 2005, Moscow’s defense reforms and ambitious armaments programs began to demand serious military-spending hikes. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute and the International Institute for Strategic Studies in London broadly agree that the Russian military budget swelled from about US$20 billion in the late 1990s to more than four times that amount in 2015, before subsiding to its current official figure of $65.9 billion (or 4.1 percent of Russia’s 2021 Gross Domestic Product). In nominal terms, this is less than a tenth of annual U.S. defense spending, but there is reason to think that these figures grossly understate the real volume of Russian military expenditures. Using Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) measures, Moscow’s effective military expenditures may be as high as $200 billion per year. In recent years, only the United States, China, and India have had defense budgets that exceed Russia’s. Russia’s State Armament Program of 2011–20 aimed to breathe new life into the defense industry by commissioning it to manufacture or refurbish 70 percent of the military’s weaponry. Official sources claim that the industry achieved this. It developed new artillery, introduced some highly accurate cruise missiles, delivered several hundred new tanks (including the highly touted T-90M), and updated hundreds more with improved armor and electronics. Almost five-hundred new fighter jets, mainly Su-27s and MiG-31s armed with radar-guided missiles, were to boost Russian airpower to a new level, with hundreds of new combat helicopters and modernized older warplanes securing Moscow’s domination of the skies. The latest State Armament Program, which began in 2020 and is to end in 2027, is more modest and focuses on advancing mobility, logistics, and the optimization and standardization of extant weapons systems. Over the past decade, Russia has become the world’s second-largest arms exporter behind the United States. Russia’s share of sales in this market from 2017 through 2021 was 19 percent while the U.S. share was 39 percent. Seeing the mediocre performance and vulnerability to Western weapons (such as the U.S.-made Javelin antitank missile) of Russian arms in Ukraine, countries that have been buying military hardware from Russia (the top three customers are China, India, and Egypt) may think twice about purchasing from Moscow again. The systemic and structural challenges that beset Russia’s defense industry are not going away. Supply-chain problems delay deliveries. Money to replace outdated machine tools and pay for research and development is lacking, while neglect of quality control is common. A recent analysis concluded: Centralized and inefficient bureaucracies, weak intellectual property rights and rule of law, poor investment climate, pervasive corruption, and insufficient funding are among the problems that hinder swift progress in fields that are particularly dependent on creating a breeding ground for creativity and the free exchange of ideas.Russian arms makers are a long way from producing weapons that can compete with Western weapons in technological sophistication and general quality. Large-scale building of precision-guided munitions, targeting systems, and heavy-strike long-range drones is beyond the reach of Russian industry. The onset of conflict with Ukraine in 2014 cost the Russian military-industrial establishment its longstanding and beneficial ties to Ukrainian weapons producers. Now sanctions have cut off Russia’s access to the Western optics and electronics that are key to advanced modern weapons. Expanding existing factories will be hard, as funds and other requisites are not there. Ambitious plans announced with much fanfare and bluster have often come to little or nothing. In 2008, the first year of military reform, there was a proposal to create autonomous mobile forces teaming airborne, naval-infantry, and special-forces components, but nothing has come of it. The widely publicized program to produce a fifth-generation fighter, the Sukhoi Su-57, is now more than twenty years old and has generated nothing but a few prototypes. The Su-57 is the first stealth aircraft Russia has ever attempted. Meant to be capable of both air-to-air and air-to-ground combat, it is supposed to be Russia’s answer to the U.S.-built Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II, thousands of which are being produced for the United States and multiple allies around the world, including nine or more NATO countries. Technical setbacks, India’s decision to pull its financing, and a December 2019 crash (the first publicly known) make it doubtful that the Su-57 will be ready for full-scale production anytime soon. Since Soviet times, the security sector has been among the most troubled parts of the economy when it comes to graft and corruption In the twenty-first century, Russia has become, in Karen Dawisha’s fitting formulation, “Putin’s kleptocracy.” Transparency International’s Corruption Perceptions Index for 2021 gave Russia a corruption score of 29, putting it far closer on the 100-point honesty scale to the world’s most corrupt country (South Sudan with an 11) than to its least corrupt (Denmark, Finland, and New Zealand with an 88 each). As defense minister, Serdyukov made it a major goal to root out or at least curb the bribery and fraud often tied to arms procurement, as well as the misuse of funds set aside to improve living conditions for the troops. Putin fired Serdyukov in 2012 because of the latter’s links to a Defense Ministry official charged with embezzlement. Large-scale corruption continues, with often hundreds of millions of dollars disappearing. A Russian military prosecutor recently admitted that about a fifth of the Defense Ministry’s budget was stolen; other officials said that it could be as high as two-fifths. Few experts would disagree with former Russian foreign minister Andrei Kozyrev’s recent claim that the corruption—and the fear of telling Putin about it—had left Russia with a “Potemkin military.”Under Arms and UnderwhelmingHow are Russian forces doing in Ukraine? It is impossible to discern precisely because most Western sources are Ukraine-friendly, while both Ukrainian and Russian media have incentives to bend the truth. That said, Russia’s military performance has been far below what most experts expected. Experts have been surprised because their assumptions were faulty. The Russian military’s track record going back to 2008 may have looked impressive on the surface, but it was compiled against weak adversaries. Georgia is very small, and its miniscule army was poorly organized to boot. In Crimea, Moscow’s troops faced little resistance. In Syria, much was made of Russian airpower’s renewed capabilities, but it was up against insurgents whose air-defense capabilities were modest at best. Russia also sent into these lesser-scale operations mostly elite troops and special forces, not average soldiers. In short, the Russian military experienced nothing like the demanding combat environment that it has met with in Ukraine. As of this writing, the war in Ukraine is almost a year old. The course of the fighting has undercut the many experts who claimed that post-2008 Russia had clawed its way into the first class of the world’s military powers. So far, Russian forces from the top down have failed most of the tests facing them in Ukraine. Military planners seldom do well to underestimate an opponent. After seizing Crimea, Putin predicted that Kyiv could be taken in two weeks; in 2022, he shrank that figure to two days. The Russian high command underestimated how many soldiers it would need to attack Ukraine while overestimating the number of locals who would welcome them. Conquering a city such as Kyiv, with its three-million people spread over 839 square kilometers split by a large river and its tributaries, would have required a massive number of collaborators. Once the plan for a quick air-mobile strike at the Ukrainian capital’s downtown collapsed amid firefights with fast-reacting Ukrainian forces at Antonov Airport northwest of the city on February 24 and 25, Russia’s campaign fell apart. Misconceived operational plans, careless logistics, and the lack of combined-arms coordination all suggest deep deficiencies in Russia’s high command. The invaders handled their tanks poorly, trying to drive them forward without proper logistical support or infantry escorts to keep Ukrainian drones and ambush teams at bay. In the skies, overcautious Russian pilots “punched below their weight,” failing to translate their superior airpower into gains on the ground. Russian troops struggled to use their communications systems and failed to disrupt their enemies’ access to satellite signals. Stories of Ukrainian soldiers using smartphones in combat to call their trainers in the United Kingdom for advice, like the ability of those defending the Azovstal steel works in Mariupol to stay in electronic touch with Ukrainian intelligence throughout the five-week siege in April and May, hint at Russian ineptitude. Troops’ general sloppiness—their neglect of small but important tasks such as properly inflating truck tires, for instance—proved costly to Russia’s war effort. As the war drags on, it is unlikely that fresh Russian officers and soldiers dispatched to Ukraine will be better prepared and equipped, or will perform better, than those whom they replace. Nuclear threats could easily backfire: If Russia were to “go atomic,” it might lose its remaining allies, misgauge wind direction and have fallout drift back over Russian territory, or find itself directly at war with a NATO alliance capable (even without nuclear weapons) of inflicting massive destruction on Russian military assets. Further, Russia’s stocks of tactical and medium-range nuclear warheads are, like many Russian weapons, Soviet leftovers. They have been sitting in scattered storage sites for decades. The work of rendering these warheads operational would involve much effort and risk of human error. There is a good chance it would also be detected by Western intelligence given the known locations of stockpiles, the limited number of units even capable (on paper) of handling and firing these warheads, and the travel distances to the theater of conflict that would be involved. The underlying theme of the assault on Ukraine has been the yawning gap between what Putin and his forces want to do, on the one hand, and what they can do, on the other. Ambition is not ability. A Revitalized Ukrainian Army Just a few years ago, Ukraine’s military itself was facing daunting challenges. An ambitious reform program was launched in 2006, but it failed amid political instability, corruption, and inadequate resources eaten by inflation and the 2008 global financial crisis. This top-down overhaul was also poorly conceived: Ukraine was striving to create an all-professional force with cutting-edge technology and advanced command and control in defiance of institutional and funding constraints. Moscow’s 2014 aggression against Crimea and the Donbas shook authorities out of this reverie and into a push for swift change in the Armed Forces of Ukraine (AFU). Under President Petro Poroshenko (2014–19), naval and defense-industry reform succumbed to infighting and embezzlement, but the creation of an autonomous special-forces command with four-thousand troops was a success. The 2014 events showed that large numbers of soldiers would be needed to defend Ukraine against Russia. The draft, abolished in 2013, was brought back in 2014. More innovatively, the AFU also became a community-based military. The financially strapped government appealed to civil society, the large Ukrainian diaspora around the world, and ordinary people to help fund the AFU and to join its ranks. New organizations cropped up “to equip, uniform, protect, and improve the Ukrainian Army as soon as possible” and to supply much-needed military equipment—their donations made up 4 percent of the Ukrainian defense budget in 2015. Another significant change that partly relieved the AFU’s manpower shortage was the creation of volunteer battalions that already by 2014 comprised more than ten-thousand fighters. While raising some disciplinary concerns, they proved effective in the conflict against separatists in eastern Ukraine and are likely to play a consequential defense role for years to come. Finally, Western countries led by the United States and Britain but also including (remarkably) Germany have sent lethal military aid that makes Kyiv’s forces measurably more effective on the battlefield. As of mid-October 2022, Washington had offered about $66 billion—a sum more than eleven times larger than Ukraine’s entire 2021 defense budget. The help has been high in both quantity and quality, including as it has sophisticated items such as U.S.-made M142 HIMARS mobile precision multiple-rocket launchers, British- and U.S.-made M777 155-millimeter howitzers, various types of UAVs, and more. Between 2015 and February 2022, active-duty British soldiers trained more than 22,000 Ukrainian recruits in western Ukraine through a program called Operation Orbital. As of September 2022, instructors from Canada, Denmark, Finland, Lithuania, the Netherlands, New Zealand, and Sweden were joining U.K. soldiers to give accelerated training to thousands more Ukrainians at camps in Britain. The programs teach junior officers, NCOs, and soldiers to think critically and make independent frontline decisions without waiting for permission from commanders sitting at distant headquarters. Ukraine’s military has been everything that Putin’s army has not. The smaller country has managed to convert its own recent reforms and massive Western aid into combat advantages. Defending their own soil, Ukrainian volunteer and professional soldiers alike have excelled in drive, courage, and resourcefulness. President Volodymyr Zelensky has been a revelation: Ukrainians are fortunate to have been led by a clear-thinking and uncompromising figure who knows that this is a contest between democracy and tyranny. The war has made Ukrainian nationhood (long denied by Russian nationalists of Putin’s type) undeniable and has underscored the larger but too-easily-forgotten truth that freedom is not free. Opposition to the invasion has also brought Western democracies closer together as members of NATO, which is adding Finland and Sweden to its ranks. If NATO continues to stand united behind Ukraine, David will have very good chances against Goliath.