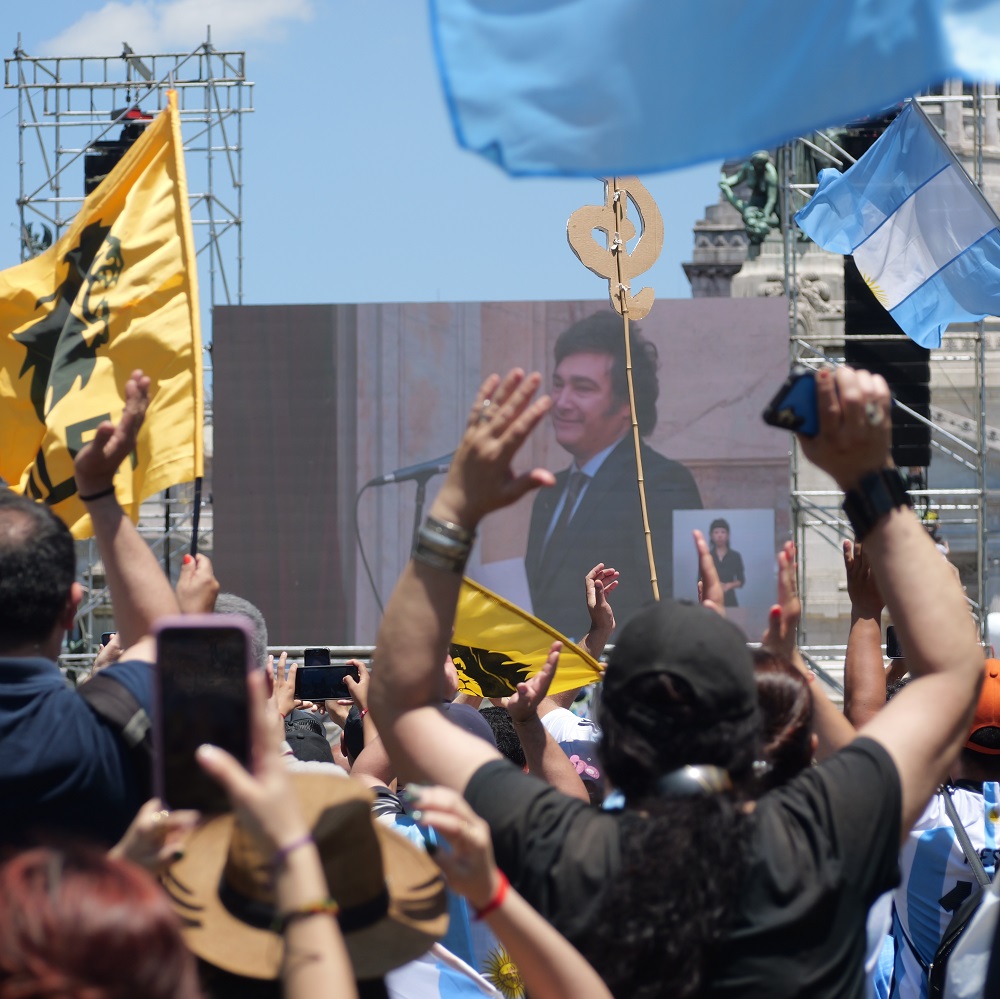
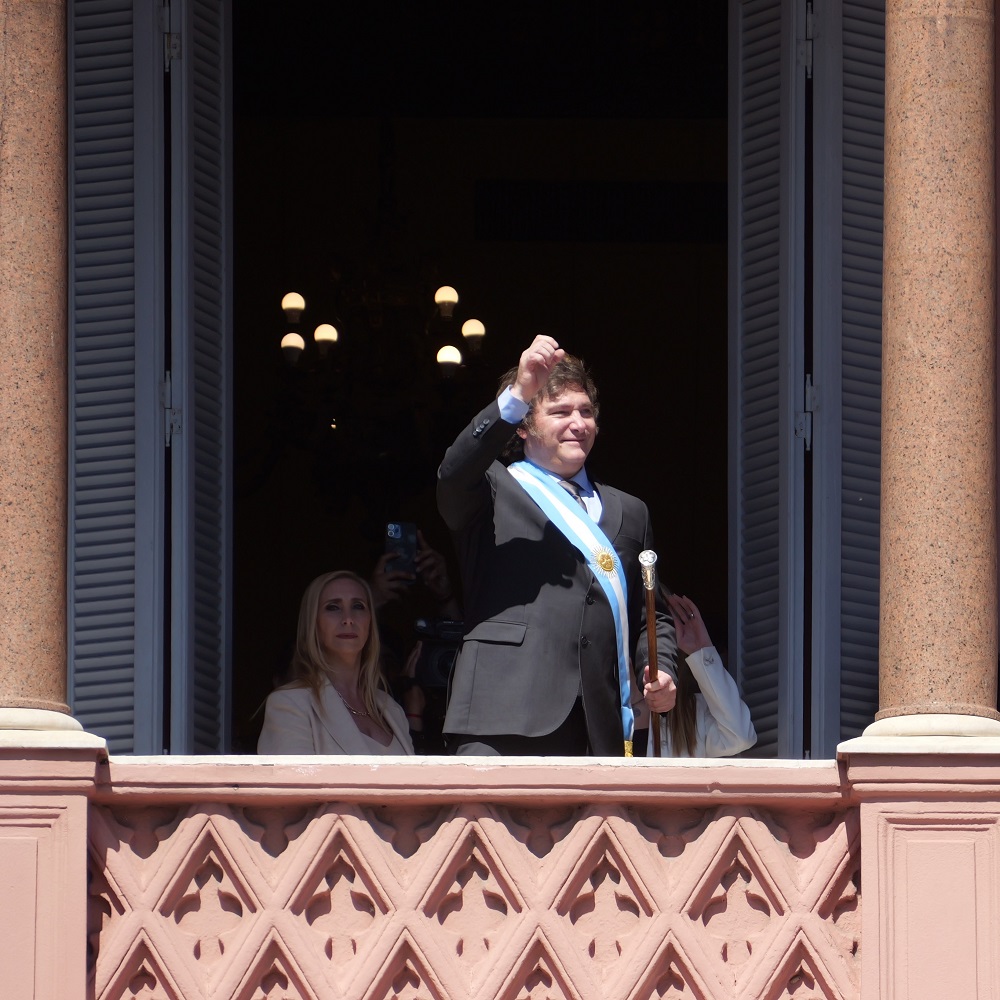
Remarks by the President of the Nation, Javier Milei, at the Economic Forum of the Americas (IEFA), at the Four Seasons, CABA
by Javier Milei
Good afternoon everyone, if we’re talking about exploring opportunities, clearly one would have to address growth issues. The problem is that, when one encounters a deeply unbalanced macro situation, growing becomes very difficult, almost I would say impossible. And especially when for many years, relative prices have been distorted and the economy has been put in an imbalanced situation, trying to live in a sort of permanent boom, when the boom comes it’s much more violent. That is why when the correction of relative prices is carried out, it generates a contraction of activity and employment, and the more violent and prolonged the process of overstimulating the economy, the stronger the contraction becomes. In that sense, Argentina has lived – for more than 20 years – under a wild populist regime, which has led to the destruction of capital, the destruction of productivity, which is why we are in an absolute miserable situation. Yes, because populism is not free; wages, in dollars, on average, in the 1990s, were $1,800 and if you adjusted for American inflation that would imply that Argentinian wages, on average, should be $3,000, something like 3 million pesos. And today, luckily, if we exaggerate and become very optimistic, we could say they are $600, which is false because they are lower. This means that Argentinians in this populist adventure have lost 80% of our income, that is the real catastrophe. The consequence of this is that we have more than 50% in poverty and 10% in extreme poverty, or a little more as well. This means that the country, which produces food for 400 million people and has a tax burden on the food production sector of 70%, meaning that the State takes the food from 280 million people, and has 5,000,000 Argentinians who do not have enough to eat, which is the real catastrophe. But it is not only a catastrophe in terms of growth, well-being, employment, and wages, but the inheritance was very complicated, the inheritance we received. I am going to describe the inheritance we received and the measures we have been taking during these first 100 days of government, and it’s not to mourn it, because the reality is that if there was something that became clear with “the Chief”is that we truly managed to win the elections it was because we were truly in a disastrous situation, because for a libertarian liberal, who openly says it, to come to power, it is precisely because the situation was not going to be an easy one. That means they were going to leave us in a very, very difficult situation, because otherwise the populists would continue to win. And for people to wake up the way they are doing, evidently it had to be a very complicated situation. So, I would almost say, we were always prepared to receive this hot potato, and you can see that, because if we hadn’t taken quick measures, we would have blown up several times already. Specifically, when studying, you review the literature on early crisis indicators, when you have twin deficits, by 4 points of GDP, it's a yellow alert; if you have 8 points of GDP it's not only a red alert, but you're going to take a significant hit. We inherited twin deficits of 17 points of GDP, just to give you an idea of the magnitude of the disaster we received. In other words, the size of the hit was going to be colossal; basically, the inheritance had the worst of the three worst crises in Argentina. It had a monetary imbalance worse than what we had before the "Rodrigazo" in 1975; we had an imbalance in the Central Bank's balance worse than what Alfonsín had at the beginning of 1989, which ended in hyperinflation, and worse social indicators than in 2001, that is, before the crisis of 2002. In other words, literally, it was the sum of all evils. In that sense, that twin deficit, of 7 points of GDP, was composed mainly of a 15-point consolidated fiscal deficit. Of those 15 points, 5 corresponded to the Treasury and 10 corresponded to the Central Bank. Furthermore, to give you an idea of the magnitude of the disaster we received, basically, although during the entire previous government, monetary issuance was used to finance the fiscal imbalance, by 28 points of GDP. Of those 28 points, 13 took place in the last year; not a minor issue if you think about it because the monetary base is already - today - 2.6 of GDP, meaning they left behind a quintupling of prices, and if you also look at the Central Bank's balance sheet having holdings in Leliqs, ranging from 30 to 90 days, meaning 30, 60, and 90 days, all converted into overnight loans, which means there was the possibility of multiplying the money supply by 4 in a day. In that context, moreover, during the first week of December, prices were rising by 1% daily, which means that in annual terms, it is 3700% inflation. If it stopped in the first two weeks, that would be 7500% annually, and if you look at what wholesale inflation was in December, which was 54%, that annualized is 17,000%. So, facing hyperinflation, if the economy had already entered a recessionary path in the second and third quarters last year but was fueled by a lot of monetary issuances to try to force an electoral outcome that did not happen, and in that context, it was essential to avoid hyperinflation. But to avoid hyperinflation, it was necessary to implement a very tough stabilization program, a program that we had and that we were only able to announce on the third day, basically because we had the issue of appointments at the Central Bank. And basically, it had the three fundamental elements that any stabilization program has, which were fiscal adjustment, exchange rate correction, and the definition of a new monetary policy. In that sense, for us, the key was to end monetary issuance so that there would be no monetary validation of the price increases, and that it would not escalate and generate hyperinflation. In that sense, along with the devaluation, which was made because basically all we did was bring the exchange rate to the market exchange rate, adjusted by the PAIS Tax, and in that context, on the fiscal front, we decided to adopt what is called a zero-deficit policy. But a true zero deficit, not a lie, meaning a zero deficit in the line of financial result, that is, after paying interests. This is very important because if we achieve a zero deficit in the financial line, it means that the debt no longer grows. And if the debt does not grow anymore, the debt-to-GDP ratio does not increase more, and therefore one becomes temporarily solvent, and the consequence of this is that the PAIS Tax begins to fall, and the interest rate will decrease. Thus, the interest rate regains its essential function, which is to be a mechanism of inter-temporal coordination and for the growth process to be related precisely to the interest rate, the natural interest rate, that is, the market rate, not the rate that a bureaucrat comes up with by meddling from the Central Bank. I clarify to make it clear, this idea of being tinkering... Once, I remember telling someone: "you are worse than Moreno" because Moreno controlled the prices of today, but you want to control the interest rate, which means you want to control the prices of today and the future. Why? Because the interest rate is the relative price of present goods over future goods. So, this would be much more complicated. So, we also began a process of cleaning up the Central Bank's balance sheet, and the reality is that we believed and aimed to achieve a zero deficit by 2024, and we were truly and absolutely committed to carrying out a fiscal adjustment, which obviously involves a lot of chainsaw and a lot of blender, and if we wanted to do it quickly, we had to use both. There is a lot of blender and much more, actually, of chainsaw because we eliminated public works outright, something of which I am deeply proud, considering that public works are a major source of corruption and theft, which I imagine all decent people should oppose. (APPLAUSE). On the other hand, we also completely eliminated discretionary transfers to the provinces; we also laid off 50,000 public employees, not only that but we also terminated contracts, and you see, now, more contracts are being terminated, and 70,000 contracts will be terminated. We also eliminated 200,000 social programs, irregularly delivered, and at no time did we neglect social policy because – in the midst of it all – we doubled the AUH; we doubled the Food Card; we tripled assistance in the One Thousand Days Plan, that is, for pregnant women, and not only that, but we also quadrupled assistance for school supplies and created a mechanism for middle-income families, who attend low-cost private schools, to have a support mechanism so that the children wouldn't drop out of school, which they attended, and not have to suffer the shock of changing schools, that is, we also had a strong social perspective in what we were doing, and we also did something that, at the time, when Minister Pettovello designed it, the red circle, which is increasingly analog and doesn't understand anything we do, because the digital era has already passed us by, but the interesting thing is that, at one point, Minister Pettovello announced that social programs didn't have to be verified as working, that is, social programs are given and they were required to provide work in return, and obviously, let's say, no one explained how the whole situation was, and then we, knowing how tough the first months were going to be, while the adjustment took place, because apart from when you generate an increase in savings and there is no counterpart of investments, it generates a drop in activity and that makes employment fall and/or real wages fall and that could lead to social tension, which we wanted to cushion. And in that sense, it's very interesting because Minister Pettovello removed the need for them to verify that they had worked. Obviously, the large number of monkeys, and I apologize to the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals for insulting the monkeys, who look at Argentinian politics, where some obviously respond that they are very angry because they don't have a guideline, but let's say those monkeys – sorry to the monkeys, again – strongly criticized Minister Pettovello for this. What they didn't realize is that it was a way to end intermediaries, where all governments wanted to end intermediaries, but this government did it. So, basically, the people who receive social programs obviously receive a card and that goes to an account. So, they thought that with that they ensured that they would not be extorted, what they didn't know is that you must go to verify if they were working and there, when you were going to receive the verification that they had been working, the Bellibonis of life appeared, taking half of people's income. And they only validated it if you brought them the pretty ones, where they must validate that they were at the rallies. I mean, in reality, they stole half of the money and not only that, but they also had to go and work as picketers, so what you were doing was finance criminals and also ruining the functioning of the streets. In that sense, by eliminating the need for a counteroffer, until April, what happened, well, those criminals could not take away the money that people received from the social program. Therefore, without spending a penny more, this implied doubling the assistance and at the same time, we set up a phone line to report the pressures and extortions of these criminals and we have received close to 300,000 reports and today there are 18,000 cases in the courts. In other words, they are going to pay for having pressured people to go to the rallies. And furthermore, Belliboni threatened us that he was going to gather 50,000 people in the Plaza, so evidently, he planned to bring 100,000. From the Nation, we contributed with 12,000 officers, I don't remember the number that the City contributed, but it was tremendous because there were more police officers than people, as only 3,000 showed up, so it was a resounding success, coordinated at that moment between Minister Bullrich, Pettovello, and the Minister of Infrastructure. Additionally, in the public transportation, there was the announcement that fare-dodging wouldn't be penalized, and the lines for making complaints, and there we also started to organize the streets. In other words, we took away their firepower because now they can't extort people to do this, and we also started to enforce order. Therefore, one of the demands we received as a government, which was to put the streets in order, we are doing it. Because now, whoever blocks the streets doesn't get paid. And moreover, whoever does it... pays for it. And that is working perfectly. Not only that, but while we expected to achieve financial balance over the course of the year, the hard work of each minister allowed us to achieve that financial surplus in the month of January. And obviously, the "red circle" – it was logical – began to predict that we would have very strong deficits in February. And to the dismay of those who live betting against those of us who want to change, we again had a financial surplus in the month of February. Specifically, what we are doing is obtaining a result that, if you take the first two months, equivalent to half a percentage point of GDP, of primary surplus, that annualized would be 6 points. Therefore, we have over-adjusted what we needed, because we only needed to make an adjustment of 5 points of GDP. It's very funny because there are many who say that this is not sustainable, that this, that, when they said that the only thing that could be done was to adjust 1 percentage point of GDP, well, we adjusted 5 percentage points, but of course, that requires a dose of courage that others do not have. But that's not all because there's also the issue of the adjustment we made within the balance of the Central Bank, which generated a 10-point fiscal deficit, quasi-fiscal, and today that number is already 4. That is, with which there is no historical record – worldwide – of a government making an adjustment of 11 points of GDP in three months. And to the dismay of the "Helicopter Club" and all those who wish us ill, especially those whose schemes we've disrupted – which are quite evident, as you'll see them complaining. There's a saying that goes, "where there's a Kirchnerist kicking, there's a scheme that's been cut off," well, it's true. And not just Kirchnerists, but also, look at some other important economic groups. You can imagine who I'm talking about. Aside from that, they're very angry because Elon Musk has arrived. The important thing about this is that faced with the inflation disaster we had when we took office, in three weeks, inflation was at 30 percent, the retail figure, and it was expected to close the month at around 45 percent. I remember one weekend, journalist Gabriel Anello, a great journalist, and an even better person, asked me about inflation, and I told him the truth, that if it stayed at 30, it was a great number because it meant that by the fourth week, prices had stopped rising. And we found that it was 25, meaning there was a retraction in prices that had been fixed from the third week to the second. Then, in January, inflation was 20 percent, and in February, it was 13 percent. Now, when you strip out the statistical carryover effects related to one-time increases, like the tariff adjustments and prepaid health plans, that's equivalent to 6 points, so the true inflation rate for February was around 7%. In other words, we're bringing the inflation rate down to single digits. Furthermore, even if you were to include all these elements in the index, but somehow capture the effect of promotions, which can't be captured by the price index because it's a non-linear pricing scheme and depends on each citizen's consumption, then it's impossible to capture through the CPI due to the effects of "two for one," "three for two," and all those things. So, there's a sort of estimation of how much that weighs, but it can't be documented, and if that effect were considered, despite the previous factors, we would still be in single digits. Furthermore, in the third week of March, the price increase came to a halt, meaning we are moving in the right direction regarding anti-inflationary policy. In fact, some of the criticisms we receive are quite peculiar because, for example, if you look at the evolution of the inflation rate, the speed of the decline is stronger than what occurred during the convertibility period. When you examine the effects of stabilization during convertibility, prices are falling much faster today, or the inflation rate is declining much faster. This also makes sense, and what happens is that during convertibility, the money supply was endogenous, meaning that when there was an increase in the demand for money, the way to validate it was to bring in dollars and sell them to the Central Bank, which implied an expansion of the money supply and allowed for the re-adjustment of relative prices to occur with upward pressure on prices. Notice that since we took office, the monetary base has practically not changed, despite buying $11.5 billion in the market. Not only that, but we also had an expansion of the money supply due to the PUCs that the previous Central Bank administration used to try to control the exchange rate, and there was also expansion due to interest-bearing liabilities. However, the contraction due to BOPREAL has been so significant that the monetary base has barely changed or changed very little. So, we still have the same monetary base of $10 billion, but now on the asset side, we have $11.5 billion more in reserves. Therefore, we are undergoing a very strong process of balancing the Central Bank's balance sheet, and soon we will have net reserves close to zero, whereas the previous government left us with $11.5 billion in negative reserves. Not only are we achieving that, but also when the demand for money is restored, since the nominal money supply is fixed, this implies that to rebuild monetary holdings, people have to sell goods. Therefore, the deceleration of price growth is much more severe than in the convertible scheme because in the convertible scheme, the money supply expanded according to the demand for money and did not conflict with the goods market, which is what causes the inflation rate to fall much faster. I also find it very amusing to those who demand changing the pace of the exchange rate evaluation, which is ridiculous because today the free exchange rate shows no gap. If I take the reference exchange rate from the Central Bank and multiply it by 1.175, which is the PAIS Tax, it would be around 1,060. Therefore, I don't have a gap; I have a negative gap. So, if the market doesn't put it elsewhere, why would I arbitrarily modify it? Based on what? On a calculation made by clueless economists because they make that calculation of the real exchange rate, and the question is, have they never seen that during crisis periods, the real exchange rate is very high, and during boom periods, it is very low? Have they not seen the trend? Have the supply and demand conditions for all goods in the Argentinian and global economy not changed? How can they pretend to be so arrogant as to determine the price of something? Moreover, they average the average. Of what? If with the standard deviation they have, that average is ridiculous. I have an article about that, which says that the real exchange rate is when economists are part of the problem. Moreover, it implies a problem of fatal arrogance or rudeness because it would imply knowing the preferences, technology, and endowments, not only of our economy but also of the rest of the world. It seems quite pathetic to believe that they can have all that information to make all those decisions. Unfortunately, in Argentina, public education - because it's all public, it can be privately managed or state-managed - has done a lot of harm by brainwashing people and leading them to read authors who have truly been disastrous for human history and especially for Argentina. I always joke that if you go to the University of Buenos Aires, to the Faculty of Economics, and ask, "Who is Ludwig von Mises?" They will tell you he's the 9th of Holland, while for others, he's the greatest economist of all time alongside Murray Newton Rothbard. But, of course, they know the bearded one, the German impoverisher Marx, they know him. But beyond this situation, the other funny thing is that if I have the future dollar curve aligned with the Crawling Peg that the Central Bank is implementing, why would I need to devalue? It's incredible, it's ridiculous. They're looking at market data and no. The whole market is wrong, they resemble James. It's incredible because when Keynesians talk about what a great investor James was... He was involved in finance and went bankrupt like a rat and the argument... if you look at Damodaran's Valuation book, there's James’s quote saying he was so arrogant that he said, "It's no use being right when the whole market is wrong. You'll lose anyway." So, everyone was wrong except him, but when they all turned against him, he lost money and went bankrupt. He had to go ask his father, who was friends with Marshall, for help, took a 6-month course, and then got into Cambridge. And when they say he was a great investor, it was all a lie because in reality, as a person with a lot of influence in English politics, he was on both sides of the counter during the War and the Great Depression. I mean, he was in both England and the United States, and Mr. James, the fortune he made, he made through what today would put him in jail, which is the inside trading. That is, he would take information from the American government, which he would use on certain things, and trade with it. It's like the movie Wall Street, Gordon Gekko was a choirboy compared to James. So, it's also another myth that he was a great investor; the guy played with classified information. I mean, nobody else thought of it, but he did. That's why all the regulations on Wall Street came afterward. So, it seems quite comical that we have to change the crawling peg when the entire futures curve is aligned with monetary policy. And in this whole context, given the commitment we have to the deficit zero policy, I often say that I've been tied to the deficit zero policy like Ulysses to the main mast, with the advantage that I have my ministers shooting at the sirens. So, we're going, and we're doing it well. So, from receiving an economy that had a PAIS risk of 2,900 points, today it's already reaching 2,400. Analysts are seeing that we're heading towards 1,000. That's not insignificant because it opens up possibilities for us to enter the capital markets. Our credit rating has been raised, bonds that used to cost $18 are now worth $54, and Argentinian assets have appreciated significantly. When you look at the GDP data today, it's true that it fell in the first quarter, by about 4.5-points, but it's also true that analysts were expecting a 6-point drop. So, we're making a much stronger adjustment than analysts anticipated, and we're falling less. And that also encourages the idea of a "V-shaped" recovery. A very interesting piece of data from the Orlando Ferreres Consultancy emerged, which is that the seasonally adjusted figure for February was positive, just a little bit. So, we're not getting excited about that number, but at least it seems that we'll be finding the bottom at some point in the near future, and many analysts are already talking about a "V-shaped" recovery, which is understandable when you look at how quickly the PAIS risk is falling. At the same time, we are working on the issue of lifting currency controls, and as soon as we manage to clean up the Central Bank's balance sheet, when we can get rid of all the interest-bearing liabilities and put an end to this nefarious practice of remunerating liabilities, what this will imply is that the issuance of money through interest-bearing liabilities will be halted. Simultaneously, another thing we are working on is a reform of the financial system to move towards an integrated system with the capital market and build a banking system that is anti-runs. The truth is, that wouldn't be a problem today because credit to the non-financial private sector is 4-points of GDP, meaning we don't have a financial system; there is no financial system. Therefore, it's interesting that we start building a financial system that doesn't require a lender of last resort. So, if that reform includes integrating the format of banks with a format of the capital market so that we can move towards a system of free banking, that will allow us, when we have that reform, to open the financial system, lift currency controls, and in that context also pass the law against monetary issuance, where basically we consider seigniorage a crime, it's theft, it's counterfeiting, it's fraud. Issuing money is a scam. And in that sense, if there were to be monetary issuance, the President of the Central Bank, the board, the President of the Nation, the Minister of Economy, and deputies and senators who have approved budgets with fiscal deficits would go to jail. Obviously, you might say to me, "But this is Argentina," and surely another criminal will come along and change things and overturn that law. But we will give it the category of non-prescriptible, as if it were a crime against humanity. Therefore, yes, another criminal may come and change these conditions and return to the practice of issuing money, but then another may come and say, "You are a criminal, you did that," and put them in jail. So, we are going for a solution of these characteristics to end this scam of monetary issuance in Argentina. And obviously, as we can continue advancing in this system of free banking, of deep capital markets moving towards a complete system, and we have stopped issuance through rediscounts, issuance through remunerated liabilities, issuance to finance the treasury, we will have a free exchange rate, with the money supply fixed, and if it is necessary for more money to enter the system, it will be entered by the agents themselves. For example, they will open their mattress and start making transactions. Therefore, the monetization of the economy will be done by individuals themselves with the currencies they want to transact. Currency competition has a very interesting consequence. For example, if you're in the oil sector like Alejandro, you can transact with your peers in WTI, or if you're in the gas business, you can transact with others in BTU. If you're in the agriculture sector, you can transact with others using soybeans in Chicago, and so on. Each will have its own currency. This is equivalent to having a basket of currencies where the weights are determined endogenously by the people, instead of being determined by a bureaucrat at their discretion, which they will always get wrong. Even if they did it right, it would have to be this result, and that's what the agents do, so we don't need a bureaucrat sticking their finger in anywhere because they already know where the finger ends up, and often, it ends up being the arm, not the finger, where they stick it. If they had a vaseline business, they would be happier celebrating. So, once we achieve this, we'll be able to lift the currency controls. Currently, we have excess demand in the Foreign Exchange Market and excess supply in the rest of the economy, resulting in low bond prices, high interest rates, and high PAIS Tax. It also means oversupply in the goods market, leading to economic activity deterioration. In fact, our per capita GDP is 15% lower than in 2011, and we have the same number of jobs in the private sector as in 2011. This implies an increase in the number of poor and indigent people, leading to social pressure for support. Naturally, when we close this excess demand in the Foreign Exchange Market, all other excess supplies will close as well. This will result in higher bond prices, lower interest rates, closing the imbalance in the goods market, economic expansion, improvements in real wages, employment, and reduction in poverty and indigence. Then, the economy will start to rebound, despite the corrupt institutions we have and the economy's deep capitalization due to over 20 years of populism. Nonetheless, we can grow and generate genuine economic growth without inflation. And we can do all of this despite the politics, despite all the obstacles, and despite all the garbage they throw at us. But you know what? There's something wonderful, something that even the analog red circle doesn't see. Every DNU issued in Argentina, all of them were aimed at generating regulations, in other words, reducing market freedom, making markets more concentrated, giving businesses to cronies, huge scams, and above all, encroaching on individual freedoms. Remember what they did during the pandemic, this gang of criminals, and yet there were people applauding them for locking us up. No one opposed that deluge of DNUs. Our DNU is the first in history to restore individual freedoms, making markets more competitive. Look at the wonderful thing in the issue of rentals; you couldn't find a property. The number of rental properties doubled, prices in real terms dropped, and the real estate market expanded strongly during the month of February. Look at the interesting things the DNU achieved, which is still in effect, but had a setback in the Senate, which, by the way, isn't so bad because if we only have seven senators and we got 25 votes, it wasn't so bad, there's improvement, there are people betting on change. But obviously, since this also touches on political scams, evidently, since politicians don't want to give up their scams, don't want to lose their privileges, don't want to give up anything, they'd rather sink Argentinians into misery to maintain their caste privileges, that's why they overturned the DNU. And this is very interesting because if I had told you that in two or three months, we were going to be able to order the Argentine ideological spectrum, you would have said I was crazy. And after what happened with the Basic Law and what happened with the DNU, it's wonderful in terms of the principle of revelation; they left all their fingers dirty. On one side, there are the orcs, who are orcs and can't be expected to behave differently because they are orcs. Then there are the people who truly want change, and there are the fraudulent criminals who say they want change, but in reality, they disguise themselves as wanting change but are just as criminal as the orcs, but they are ashamed to be associated with them. So, they hide behind formalities and all those issues, but deep down, they are the same garbage as the orcs. It was very interesting because it became evident, both in the voting in the House, particularly on the articles, and in the Senate the other day, they were exposed. Today, with the vote, it became clear who is against progress, who the criminals are, who are in favor of scams and theft, and who are against returning freedom to the people, against competitive markets, and against letting go of the scams so that people can get their money back. So, it's wonderful because in three months, we ended up unmasking these criminals. And that's also very interesting because it won't come for free in the midterm election; they will pay with their votes, and those criminals will be left out. That will allow us to have a much better midterm election than the one we had last year. That's interesting because we'll have another composition of Congress, and all the reforms that we couldn't push through now, we'll do it at that time, starting on December 11th, 2025. Furthermore, we'll push through the 3,000 pending reforms that we couldn't pass because of this group of criminals who are the obstruction machine, who want the status quo to continue, where you pay the bill, and they benefit. Therefore, I am very optimistic about the future because we are achieving a lot of things despite politics, and people are seeing that. It's very interesting because even though we are facing the largest adjustment in the history of humanity, with 70% of Argentinians acknowledging that they are worse off... There are some very important data points. The first one is that when we took office, only 20% of Argentinians believed they would be better off in a year's time, but in January, that number rose to 30%, in February it climbed to 42%, and today it stands at 50%. This means that despite being worse off in the present, 50% of Argentinians are convinced that we will be better off from now on. Not only that, but 70% of Argentinians are convinced that we will defeat inflation, with 50% of them believing we will do it in the first year and 20% believing we will do it in the second year. When you look at what's happening in terms of a word that represents the sentiment of Argentinians, the word that appears most strongly and fundamentally dominates is "Hope". Yes, people have "Hope", people see that we are going to make it. There is light at the end of the tunnel, and people are seeing it, even though they are going through a tough time now. They've realized that populism leads nowhere, they've realized that the solution lies in embracing the ideas of Liberty, and that's no small feat. If today were the elections in a runoff, we would be getting 58%, that is, it would be 58, 42. Instead of +2, we are +16, and when you ask that group: Who would you vote for in the first round? They would vote for ‘Libertad Avanza’ with 48%, that is, we improved the voting strength by 60% compared to what we obtained. This means that with that alone, we would already win in the first round because the second person in voting intention is Mrs. Cristina Fernández Kirchner with 20%. But not only that, there are 10 points, which if we go for the most rudimentary case, half and half, 48 and 5 = 53. Therefore, what I want to tell you is that there is hope. Do you know why there is hope? Because people woke up, they decided to stop being sheep and decided to be Lions now. Therefore, there is hope because Argentinians are embracing the ideas of freedom, not only that I'm going to tell them that we're going to be better, but they also already know that we're going to be better. Therefore, Argentina does have a future because that future is liberal. Thank you very much.