Hyper-Presidentialism and Human Rights: Uzbekistan’s domestic and international political profile
by Joel Moffat
As its constituent states emerged from the ruins of the Soviet Union, Central Asia has often struggled to balance both its inter-state hostilities and surrounding international geopolitical competition. While all five states have adopted remarkably different means to navigate this challenging context, largely the region has proven victim to the excesses of authoritarian and despotic regimes. The inheritance of a distorted Soviet-era centralisation and the prevalence of lucrative natural resource deposits has facilitated this unfortunate state of affairs across the region.
Uzbekistan is no exception in this regard, with an increasingly hardline hyper-presidential system. Covering much of the land between the Caspian sea and the Pamir Mountains, the region’s most populous country is emerging into a critical regional player. Under both leaders since independence, the country has attempted to balance its geopolitical profile to ensure state and regime security. It has attempted to ensure this whilst perpetuating an economic system and domestic political establishment that ensures the perpetual poverty of the population. Faced with both an increasingly challenging regional environment and greater interest from external parties, the future Tashkent carves out for itself has critical implications for that of the region.
Politics and Poverty in Uzbekistan –
Uzbekistan’s domestic politics are defined fundamentally by hyper-centralisation. The geographical unitary power structure, with minimal rates of devolution are indicative of this approach. The tendencies for hyper-centralisation are clearly inherited from the Soviet era. State power is highly concentrated in the executive branch. Ostensibly Uzbekistan is a democratic country, constitutionally allowing for a proliferation of distinct political parties. However, requirements of state-registration severely curtail the development of regional parties, with every new party requiring a minimum number of signatures throughout the whole country. This highly bureaucratic system for party registration ensures there is no effective opposition within the Olij Majlis (Uzbek Parliament).
The shadows of Soviet history also appear within the economic construction of the state. Nearly all major strategic industries remain under the control of state-owned companies. This has ensured skewed economic development, producing a significant bias for the more urbanised and industrialised eastern regions of the country, whilst leaving peripheral regions perpetually poverty-stricken. Police barriers along inter-urban roads and mandatory population registration restrict internal economic migration. The environmental destruction of the Aral Sea has left Karakalpakstan the most deprived and destitute of all these peripheral regions. As the singular grantee of an autonomous status from Tashkent, the area holds a unique position within the domestic Uzbek political establishment. This is in spite of the consistent efforts by the government to complete the centralisation of the state. In 2022, attempts to revoke the region of its autonomous status resulted in protests that saw 18 people killed, and hundreds more wounded or detained. Despite Mirziyoyev decision to pull back on this, the violent reaction towards the protests indicates the great degrees of subjugation and desperation the region remains under. Despite the better attempts by propaganda to ensure the image of the State as the singular guarantor of peace and security, frustration is felt everyday through the lack of substantial opportunities and persistent security sweeps .
Foreign Policy of Karimov –
Islam Karimov quickly rose to power from the collapse of Soviet rule. Prior to independence, Uzbekistan was characterised by very few nationalist popular movements, with independence really occurring as a sudden moment. Indeed, the initial reluctance was shown to break from the Soviet Union. From Moscow, Karimov inherited a highly centralised political establishment. This provided the blueprint for the hyper-presidential system he doggedly maintained throughout his presidency.
The most important foreign policy directive for Karimov was to ensure a strategic balance of larger powers. Despite ostensibly securing the maintenance of the country’s sovereignty, the most important motive for Karimov was the preservation of his personal regime. This focus on strategic balancing primarily emerged from a structural paranoia. Perceived regime threats became especially pertinent with the rise of the ‘Colour Revolutions’. Tashkent’s relation with the US declined dramatically following American support for these movements in analogous states (Georgia, Ukraine, Kyrgyzstan). The direct US criticism of the state’s role in the Andijan massacre, ensured Karimov saw deepening relations with DC as a threat to regime survival. The Andijan massacre saw 700 civilians killed by security forces over fears of rising Islamist movements. Re-engagement with Russia escalated during its aftermath as Moscow promised to reject all calls for independent investigation.
Foreign Policy of Mirziyoyev –
Following the death of Karimov in 2016, Mirziyoyev quickly positioned himself as the state’s successor. The initial months of Mirziyoyev’s presidency were treated with a great deal of excitement from those wishing for reform. He publicly vowed to address the states dismal human rights record, beginning with reforms for the rule of law and transparency in courts. Most importantly he abolished the practice of forced labour for large swathes of the population in the country’s vast cotton fields, a practice representing one of the greatest instances of slave labour in the modern world. This potential era of reform was quickly brought to an unfortunate end. Following an 87.1% majority in a snap election last year, Mirziyoyev initiated a series of reforms that extended the presidential term limit from five to seven years and removed term limits.
Since coming to office, Mirziyoyev has pursued a distinctly expansive and open approach to foreign relations, especially compared to his predecessor. Whereas both can be defined by pragmatic use of strategic balancing, the methods both presidents have used to achieve this have been remarkably differently. Indeed, Mirziyoyev considered his predecessor’s foreign policy as a major economic and security constraint for the state. Whilst Karimov focusses on utilising a singular larger power at one time, Mirziyoyev sees greater utility in a simultaneous multilateral approach. This has had a notable regional effect, as Uzbekistan has engaged with neighbours previously ignored in the state’s foreign policy. For example, a visa program has been initiated for short term stays for Kyrgyz people living in the cross-border communities in the Fergana Valley. As with other Central Asian states, many ethnic Uzbek communities remain separated from Tashkent due to the complications of drawing post-Soviet border demarcations. Where this has caused significant regional hostilities, most notably with the consistent violence across porous Kyrgyz-Tajik border, Uzbekistan has chosen to not claim any of these communities. The new president has also initiated new strategic engagement with Tajikistan, with which relations remained frozen for two decades due to water security issues. Uzbekistan has further expanded its close allies, with a Turkish-Iranian-Pakistani summit held in Tashkent last year. In this regard, the new foreign policy initiated under the presidency of Mirziyoyev represents an expansion of multilateral relations without focussing too much on the pursuit of one singular relationship.
The Future of Uzbek Strategic Balancing –
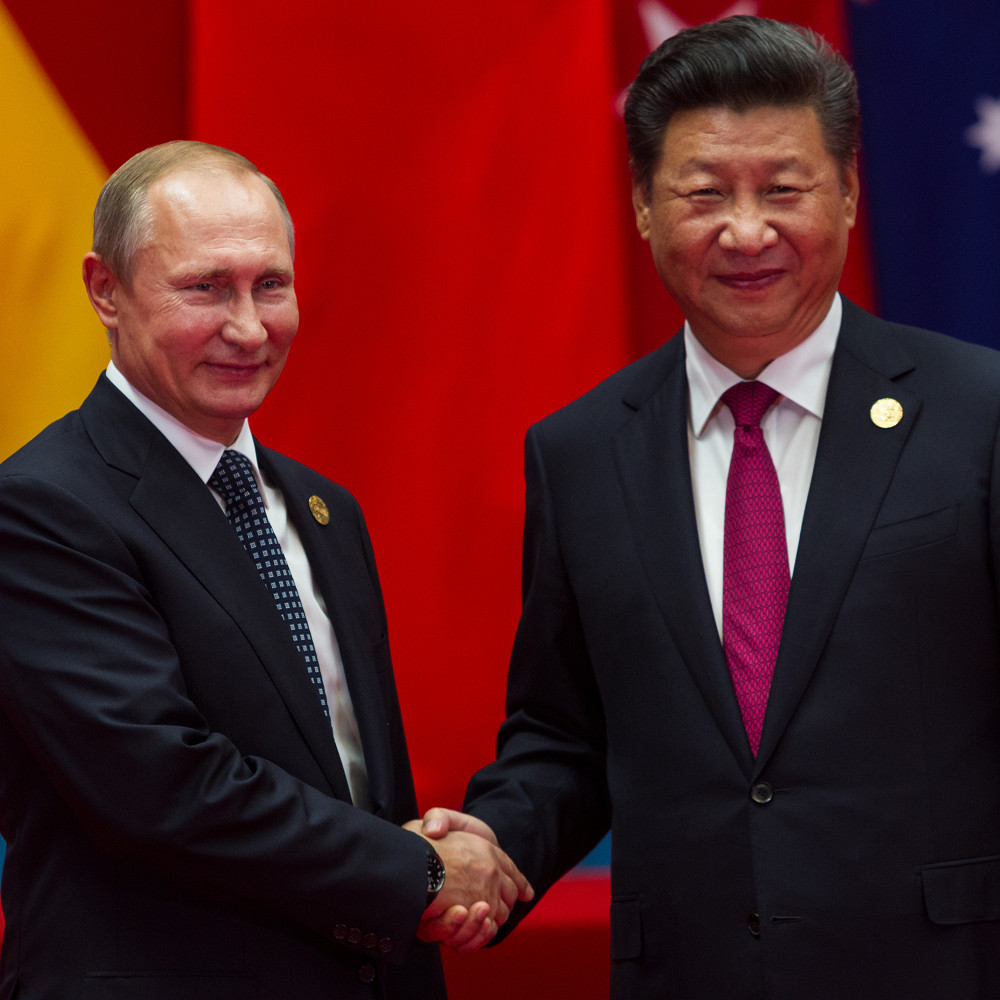
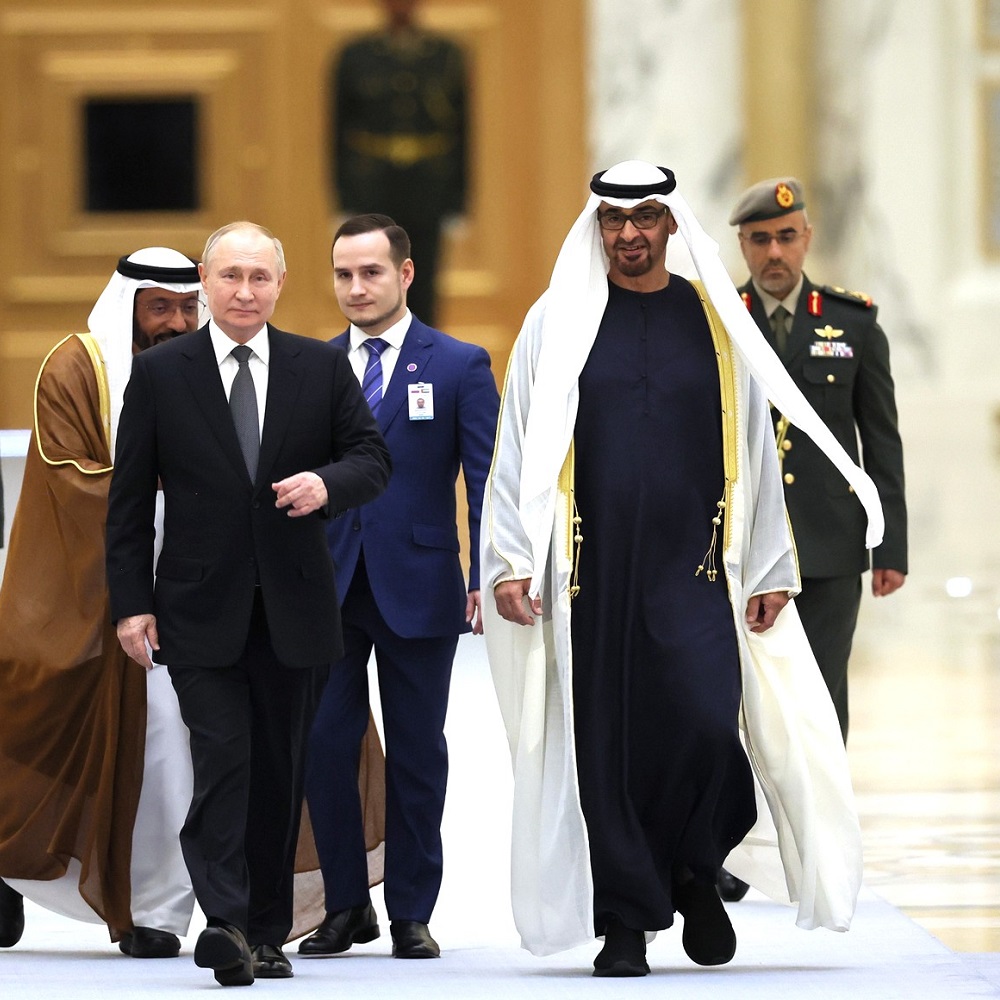
The future of Uzbekistan’s foreign policy is dependent on how it manages its strategic partnerships moving forward. Mirziyoyev has made important moves to increase regional outreach. However, the most important relations still pertain to the larger powers. A Sino-Russian rivalry over Uzbekistan has long been predicted by analysts. In the immediate picture, China appears to be the more lucrative option for the President. Offering financial aid and infrastructure investment bereft of the implied threats to regime survival that initially undermined Tashkent’s relation with Washington. Russia continues to suffer financial restrictions from the ongoing Ukrainian invasion. Remittances from migrant workers, an agreement that previously held significant mutual benefit, have declined rapidly. Indeed, the most important human factor in relations now appears to be the mass emigration of Russians leaving to avoid the Moscow draft. Last year, US Secretary of State Anthony Blinken also completed a large diplomatic effort to draw Central Asian leaders closer to the US and to ensure these states aren’t used by Russia to evade Western sanctions. It is unlikely that Uzbekistan will take a hardline stance against Russian aggression, but the declining utility of Moscow as a strategic partner does indicate a shift of relations. In this regard, Uzbekistan will continue to retain its relations with Russia, but will enlarge and diversify its portfolio of engaged actors. Following the Mirziyoyev foreign policy pursued so far, beneficial relations with regional neighbours will remain an important development but the manner in which Tashkent manages its larger partnerships will be critical to the country’s future.
More about this:
Bibliography –
• Anceschi, Luca. "Integrating Domestic Politics and Foreign Policy Making: The Cases of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010): 143-158
• Dadabaev, Timur. "Uzbekistan as Central Asian Game Changer? Uzbekistan’s Foreign Policy Construction in the Post-Karimov Era." Asian Journal of Comparative Politics 4, no. 2 (2019): 162-175
• Gulyamova, Lola. The Geography of Uzbekistan: At the Crossroads of the Silk Road. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2022
• Laruelle, Marlene. Constructing the Uzbek State: Narratives of Post-Soviet Years. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books, 2017
• Spechler, Dina Rome and Martin C. Spechler. "The Foreign Policy of Uzbekistan: Sources, Objectives and Outcomes: 1991-2009." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010): 159-170
• Yilamu, Wumaier and SpringerLink (Online service). Neoliberalism and Post-Soviet Transition: Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018
References-
1 Yilamu, Wumaier and SpringerLink (Online service). Neoliberalism and Post-Soviet Transition: Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 59
2 Yilamu, Wumaier and SpringerLink (Online service). Neoliberalism and Post-Soviet Transition: Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 59
3 Gulyamova, Lola. The Geography of Uzbekistan: At the Crossroads of the Silk Road. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2022, 152
4 Spechler, Dina Rome and Martin C. Spechler. "The Foreign Policy of Uzbekistan: Sources, Objectives and Outcomes: 1991-2009." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 165
5 https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jul/04/uzbekistan-regional-state-of-emergency-deadly-unrest-karakalpakstan-autonomy
6 Laruelle, Marlene. Constructing the Uzbek State: Narratives of Post-Soviet Years. Lanham, Maryland: Lexington Books, 2017, 72
7 Yilamu, Wumaier and SpringerLink (Online service). Neoliberalism and Post-Soviet Transition: Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 48
8 Spechler, Dina Rome and Martin C. Spechler. "The Foreign Policy of Uzbekistan: Sources, Objectives and Outcomes: 1991-2009." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 164
9 Anceschi, Luca. "Integrating Domestic Politics and Foreign Policy Making: The Cases of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 145
10 https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2015/5/12/uzbekistan-10-years-after-the-andijan-massacre
11 Anceschi, Luca. "Integrating Domestic Politics and Foreign Policy Making: The Cases of Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 152
12 https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2018/10/14/on-the-reform-path-uzbekistan-opens-up-after-years-of-isolation
13 https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/7/10/uzbek-president-re-elected-for-seven-year-term-in-snap-election
14 Dadabaev, Timur. "Uzbekistan as Central Asian Game Changer? Uzbekistan’s Foreign Policy Construction in the Post-Karimov Era." Asian Journal of Comparative Politics 4, no. 2 (2019): 165
15 Spechler, Dina Rome and Martin C. Spechler. "The Foreign Policy of Uzbekistan: Sources, Objectives and Outcomes: 1991-2009." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 160
16 Spechler, Dina Rome and Martin C. Spechler. "The Foreign Policy of Uzbekistan: Sources, Objectives and Outcomes: 1991-2009." Central Asian Survey 29, no. 2 (2010), 160
17 Dadabaev, Timur. "Uzbekistan as Central Asian Game Changer? Uzbekistan’s Foreign Policy Construction in the Post-Karimov Era." Asian Journal of Comparative Politics 4, no. 2 (2019): 167
18 https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/11/9/pakistan-turkey-iran-leaders-visit-central-asia-in-diplomatic-push
19 Dadabaev, Timur. "Uzbekistan as Central Asian Game Changer? Uzbekistan’s Foreign Policy Construction in the Post-Karimov Era." Asian Journal of Comparative Politics 4, no. 2 (2019): 170
20 https://www.nytimes.com/2023/02/27/world/asia/blinken-china-russia-ukraine-war.html?searchResultPosition=9
News Sources –
https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2018/10/14/on-the-reform-path-uzbekistan-opens-up-after-years-of-isolation
On the Reform Path: Uzbekistan opens up after years of isolation (2018).
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/11/9/pakistan-turkey-iran-leaders-visit-central-asia-in-diplomatic-push
Pakistan/Turkey/Iran Leaders visit Central Asia in Diplomatic Push (2023)
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/7/10/uzbek-president-re-elected-for-seven-year-term-in-snap-election
Uzbek President re-elected for Seven Year Term in Snap Election (July 2023)
https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2023/5/12/uzbekistans-president-seeking-to-extend-grip-on-power-analysts
Uzbekistan’s President Seeking to Extend Grip on Power: Analysts
https://www.aljazeera.com/features/2015/5/12/uzbekistan-10-years-after-the-andijan-massacre
Uzbekistan 10 Years After the Andijan Massacre
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/02/27/world/asia/blinken-china-russia-ukraine-war.html?searchResultPosition=9
In Central Asia, Blinken Will Urge Distance from Russia, and Ukraine War (2023)
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jul/04/uzbekistan-regional-state-of-emergency-deadly-unrest-karakalpakstan-autonomy
Uzbekistan Imposes Regional State of Emergency after Deadly Unrest –